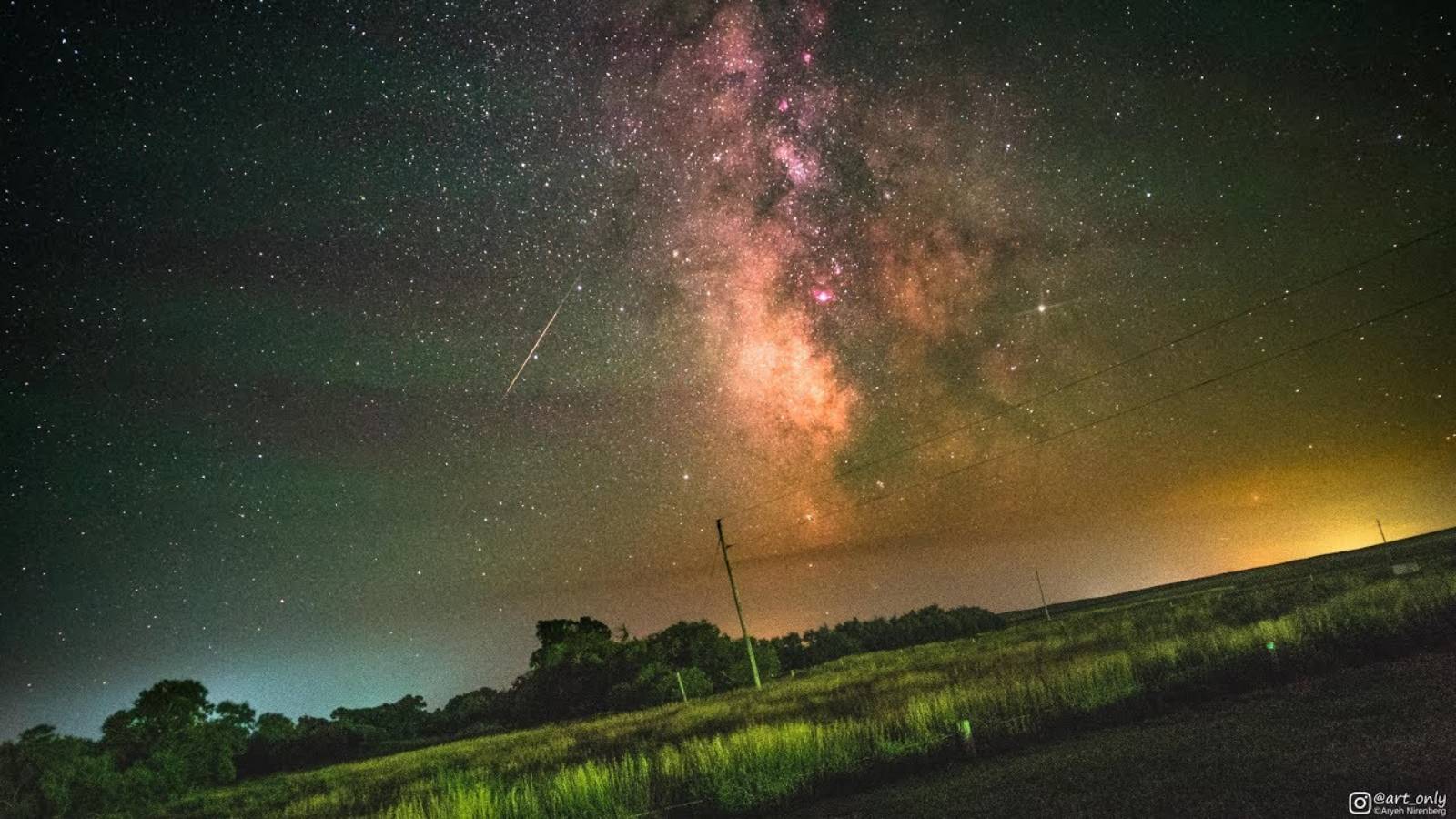
Milky way. Stunning new images of our galaxy have been published by ESA, the European Space Agency, and we're talking about a surprising presentation of everything that exists within it at this moment. You can see in these images of the Milky Way the star groups that exist in the galaxy of which we are a part, ESA managing to capture quite clearly the most important formations that many astronomers are monitoring now.
Milky way. Using the Gaia observatory, ESA managed to capture families of stars in our galaxy, all grouped in truly impressive formations, which reveal how much diversity there is. Those from ESA also discovered that all the stars in the Milky Way that formed in similar periods, based on the same gas formations, have remained together until now, being compared to human families.
Milky way. New AMAZING Images that also IMPRESSED ESA
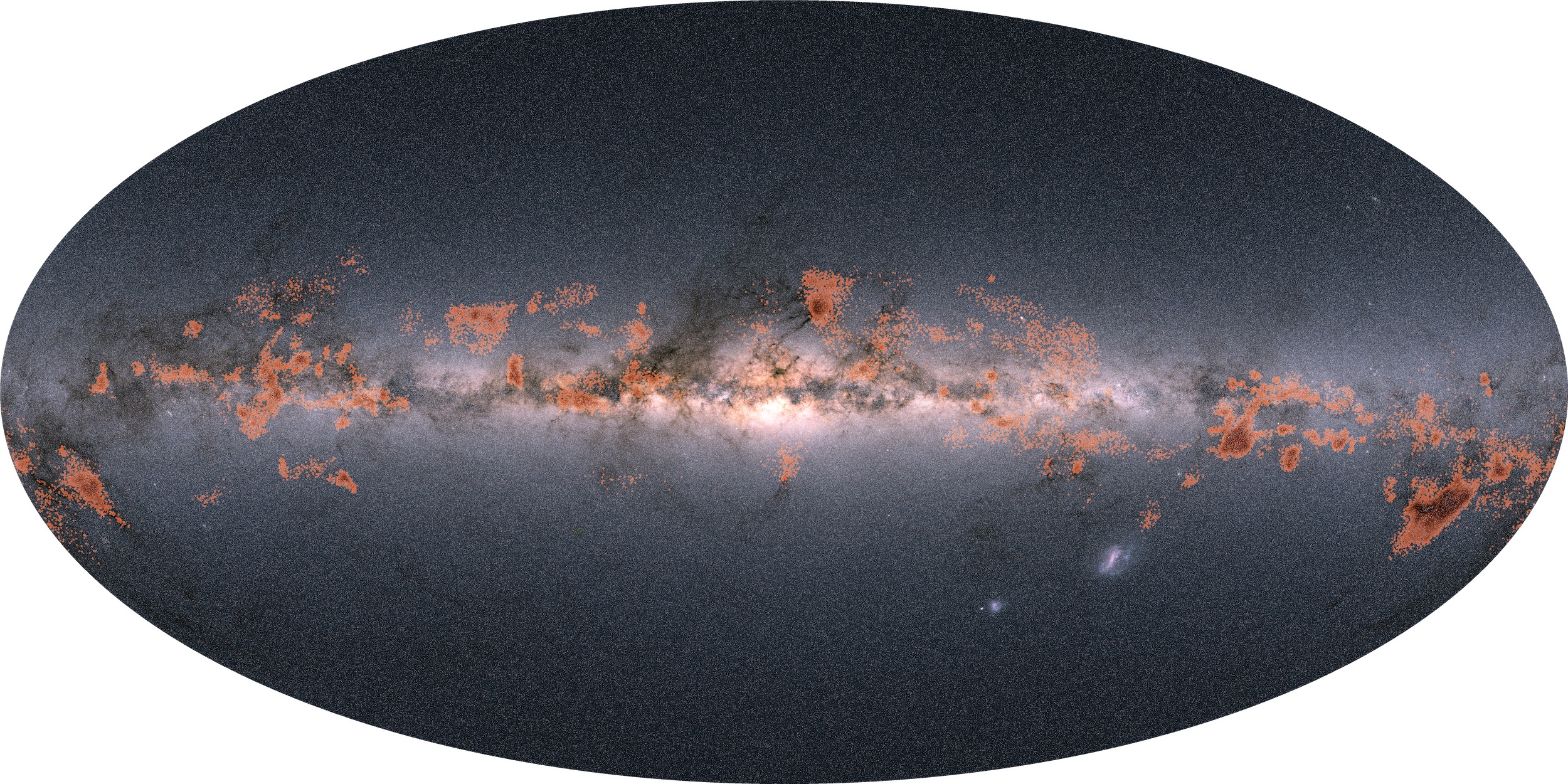

Milky way. ESA researchers believed that stars move away from each other shortly after formation, but in reality they remain in the same formations even up to 1 billion years. No less than 2000 "families" of stars that had not been previously identified in the Milky Way were analyzed, they being over 3000 light-years from the Earth, and thus it was discovered which are part of the "families", or not.
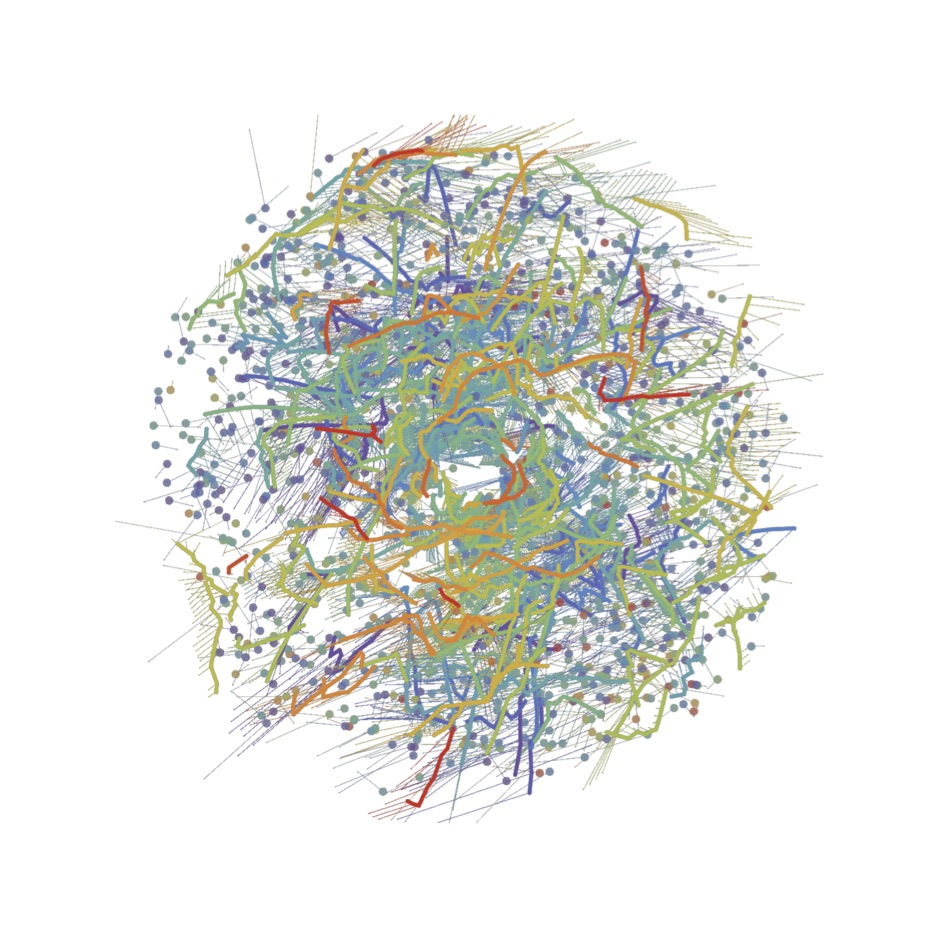
"To identify which stars formed together, we look for stars that move in a similar way, as all stars that formed within the same cloud or cluster would move in a similar way. We generally believed that young stars would leave their birthplaces only a few million years after forming, completely losing ties to their original family. But it turns out that stars can stay close to their siblings for as long as a few billion years. "
Milky way. The identification of their age also helped to identify the "families" of stars, in this way the researchers were able to figure out which were formed in extremely close periods, and remained together. All these analyzes managed to demonstrate that in the Milky Way, and most likely in other galaxies, there are many star formations that have been together since the moment they appeared, and until now.
Milky way. Although our galaxy is small compared to many others in the universe, there are still many unknowns within it, such as the thousands of stars discovered and analyzed now.

















