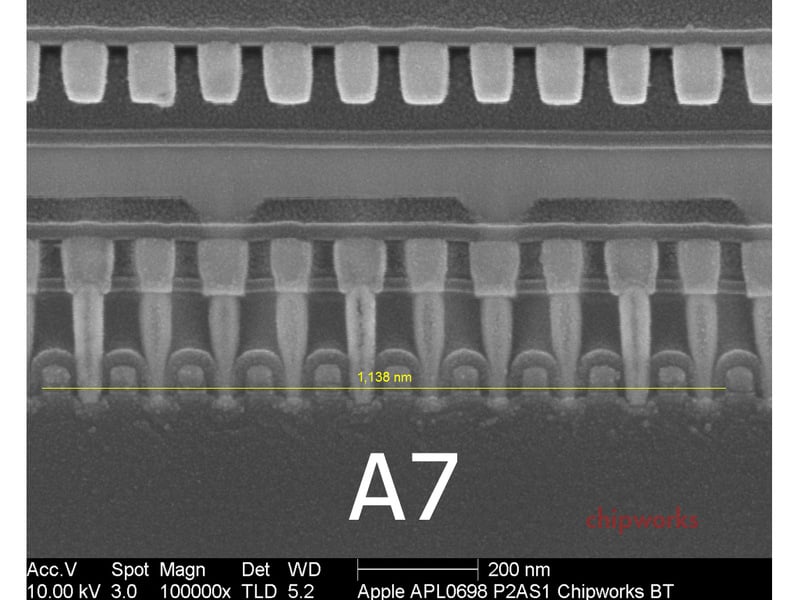
Those from Chipworks they analized in detail the face A7 al iPhone 5S and other components of the new terminal, even managing to photograph the inside of the chip designed by the American company. Without surprising too many people, those from Chipworks claim that this component is produced using a 28nm manufacturing process, in recent months there have been countless rumors indicating this. If you're wondering where some of the higher processing power comes from, well the distance between each transistor on the chip A7 is 114 nanometers, compared to the 123 nanometers measured for the A6 chip.
The "gate pitch," or distance between each transistor, inside the A7 is 114 nanometers, smaller than the 123-nanometer distance found in the A6. That allows Apple to pack as much power as the A6 into an area 77 percent as large. But the A7 chip uses an even larger amount of total space than the A6, which means the extra space offered by the 28-nanometer process has allowed Apple to significantly improve the performance of its latest mobile processor.
The use of the 28nm manufacturing process provided those from Apple Lossless Audio CODEC (ALAC), and the possibility of improving the energy efficiency of its new face, it being presented as a great evolution compared to the previous model. So far iPhone 5S it was classified as the fastest smartphone in the world, according to the first benchmarks, and this A7 chip is the basis of its very good performance.