La Cupertino inginerii companiei Apple lucreaza constant la dezvoltarea de tehnologii noi si astazi am pentru voi una care are menirea de a imbuntati calitatea ecranelor implementate in iDevice-uri. Apple isi propune sa dezvolte un nou model de ecran care isi optimizeaza calitatea in functie de mediul inconjurator si de pozitia utilizatorului. Noul ecran gandit de Apple foloseste senzori din iDevice-uri pentru a percepe lumina ambientala si pozitionarea utilizatorului pentru a isi modifica luminozitatea sau pentru a genera umbre dinamice pe continut, totul in ideea de a imbunatati calitatea imaginilor oferite utilizatorilor.
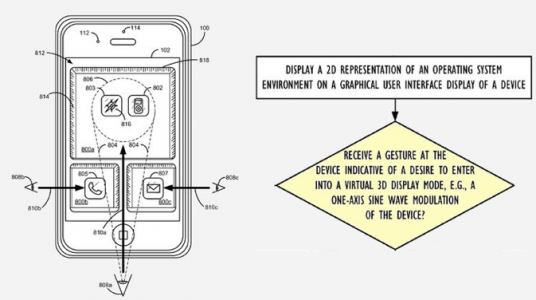
Apple’s invention is about the use of various position sensors, e.g., a compass, a Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) accelerometer, a GPS module, and a MEMS gyrometer, to infer a 3D frame of reference (which may be a non-inertial frame of reference) for a personal electronic device, e.g., a hand-held device such as a mobile phone. Use of these position sensors could provide a true Frenet frame for the device, i.e., X- and Y- vectors for the display, and also a Z-vector that points perpendicularly to the display. In fact, with various inertial clues from an accelerometer, gyrometer, and other instruments that report their states in real time, it is possible to track the Frenet frame of the device in real time, thus providing a continuous 3D frame of reference for the hand-held device.
Umbrele dinamice ar putea fi afisate fie pentru a pune in prespectiva continutul fie pentru a evidentia doar continutul la care se uita utilizatorul, deci vorbim despre implementarea unor senzori capabili sa calculeze pozitia ochilor si continutul pe care se concentreaza utilizatorul. Tehnologia companiei Apple poate fi utilizata atat in iPhone-uri cat si in tablete iPad sau chiar laptop-uri insa ea pare a fi scoasa dintr-un film stiintifico-fantastic si inca departe de a fi implementata intr-un dispozitiv desi la CES am vazut un Windows 8 controlat doar folosind ochii.
Once the continuous frame of reference of the device is known, the techniques that will be disclosed herein could then either infer the position of the user’s eyes, or calculate the position of the user’s eyes directly by using a front-facing camera. With the position of the user’s eyes and a continuous 3D frame-of-reference for the display, more realistic virtual 3D depictions of the objects on the device’s display may be created and interacted with.