Cu doar cateva luni in urma a fost descoperit un bug periculos in Safari pentru iOS, acesta permitand hackerilor sa profite de naivitatea utilizatorilor pentru a ii pacali si a le fura datele personale. Tehnica numita web page spoofing permitea hackerilor sa cloneze interfata unui website si sa pacaleasca un utilizator cu un email, acesta fiind directionat catre website-ul hackerului care arata identic cu altul real, in care utilizatorul are incredere. Tehnica presupune inclusiv crearea unui URL extrem de asemanator cu cel al website-ului real, sau ascunderea acestuia prin manipularea modului in care este vizualizata pagina, problema fiind rezolvata intr-un final de catre Apple.
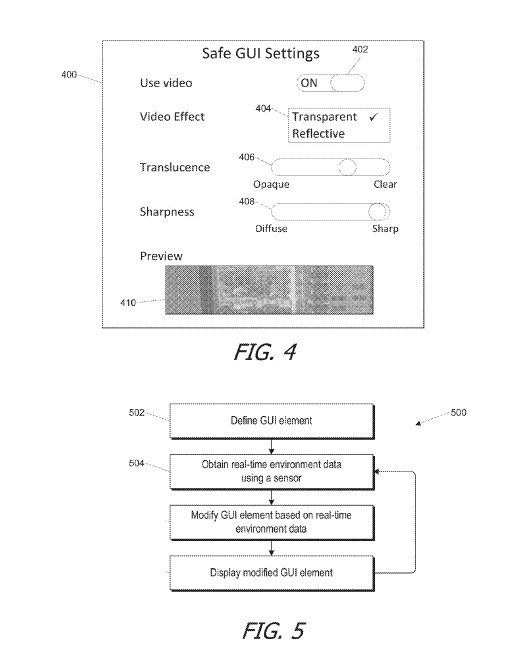
In some embodiments, the GUI can incorporate different levels of image detail. For example, the background area of the GUI can be rendered in an average color based on the real-time image data. In some embodiments, a global average of the pixel colors of the image is computed and used to determine the background color. In other embodiments, a local weighted average is taken over each of a number of sections and used to color pixels in that section; pixels near the edges of sections can be blended for a smoother transition.
Chiar daca problema a fost atunci rezolvata, Apple este constienta ca probleme de acest gen pot sa reapara oricand, asa ca ea dezvolta metode prin care aceste probleme pot fi in mare masura evitate. Tehnologia celor de la Apple presupuneutilizarea camerei, a microfonului si a altor senzori din iDevice-urile noastre, acestia actualizand in mod constant interfata grafica a unui website pentru a verifica daca ea este sigura pentru utilizare. Desi cei de la Apple par hotarati sa ofere metode sigure de navigare pe internet, ramane de vazut cand sau daca vom avea aceasta tehnologie disponibila in iDevice-uri.